概要
docker run -p 8888:80 alpineを実行した時に、iptables を使って実際にどのような設定が行われているかを確認してみようというブログである。
本編
なにはともあれ、まずはコンテナを起動。
ubuntu@network-vm:~$ docker run -dti -p 8888:80 alpine /bin/sh
Unable to find image 'alpine:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/alpine
6e174226ea69: Already exists
Digest: sha256:4bcff63911fcb4448bd4fdacec207030997caf25e9bea4045fa6c8c44de311d1
Status: Downloaded newer image for alpine:latest
72e67b28c53b725599343088e73a280668acd2ecf18b5a1ee50a486ee0bbdf31iptablesを見てみる。iptablesコマンドはデフォルトの表示はFILTERテーブルなのでnatテーブルに関しては後述する。
ubuntu@network-vm:~$ sudo iptables -L -nv
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1095 5894K DOCKER-USER 0 -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
1095 5894K DOCKER-FORWARD 0 -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain DOCKER (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT 6 -- !docker0 docker0 0.0.0.0/0 172.17.0.2 tcp dpt:80
0 0 DROP 0 -- !docker0 docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain DOCKER-BRIDGE (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
2 120 DOCKER 0 -- * docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain DOCKER-CT (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
668 5853K ACCEPT 0 -- * docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
Chain DOCKER-FORWARD (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1095 5894K DOCKER-CT 0 -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
427 41758 DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 0 -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
427 41758 DOCKER-BRIDGE 0 -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
427 41758 ACCEPT 0 -- docker0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
425 41638 DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 0 -- docker0 !docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DROP 0 -- * docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain DOCKER-USER (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1095 5894K RETURN 0 -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0Chain(チェイン)はルールを適用するタイミングで以下の5つがある。
- INPUT:パケットを受信した時に適用
- OUTPUT: パケットを送信した時に適用
- FORWARD: パケットを転送した時に適用
- PREROUTING: パケットを受信してルーティングする時に適用
- POSTROUTING: パケットを送信しルーティングした後に適用
チェインは独自に作成することができ、今回注目するのはDockerチェインである。 targetはルールに一致したパケットに対してどのようなアクションを取るか定義している。(ACCEPTは通過、DROPはパケットを破棄など)
今回見たいところを抜粋すると以下。
Chain DOCKER (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT 6 -- !docker0 docker0 0.0.0.0/0 172.17.0.2 tcp dpt:80inが!docker0なのでdocker0、つまり仮想L2ブリッジ以外の送信元アドレス。
outがdocker0なので、docker0に向かう通信のうち、宛先IPアドレスが172.17.0.2でポートが80のパケットがACCEPTされるということ。
(docker0とは、Dockerのデフォルトの仮想L2ブリッジ)
この時点でコンテナのIPである172.17.0.2の80番ポートにパケットが流れるのでコンテナのポートは80ということになるが、せっかくなのでnatテーブルも確認する。
natテーブルを見てみると以下。
ubuntu@network-vm:~$ sudo iptables -L -nv -t nat
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
5 380 DOCKER 0 -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DOCKER 0 -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 !127.0.0.0/8 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
10 622 MASQUERADE 0 -- * !docker0 172.17.0.0/16 0.0.0.0/0
Chain DOCKER (2 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 RETURN 0 -- docker0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 DNAT 6 -- !docker0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:8888 to:172.17.0.2:80
これも関係する箇所を抜粋すると以下である。
Chain DOCKER (2 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 RETURN 0 -- docker0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 DNAT 6 -- !docker0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:8888 to:172.17.0.2:80DNATの設定が追加されており、inが!docker0なのでdocker0以外の送信元かつ8888ポートに来た通信の場合は172.17.0.2:80を通るように設定されている。
つまり、ホストの外側からコンテナ内部にアクセスするNAPT(宛先のみ変換するので実際にはDestination NAT)が設定されている。
ちなみに172.17.0.2はコンテナ自体のIPアドレスである。実際にinspectコマンドで確認すると以下。
docker inspect 72e67b28c53b725599343088e73a280668acd2ecf18b5a1ee50a486ee0bbdf31
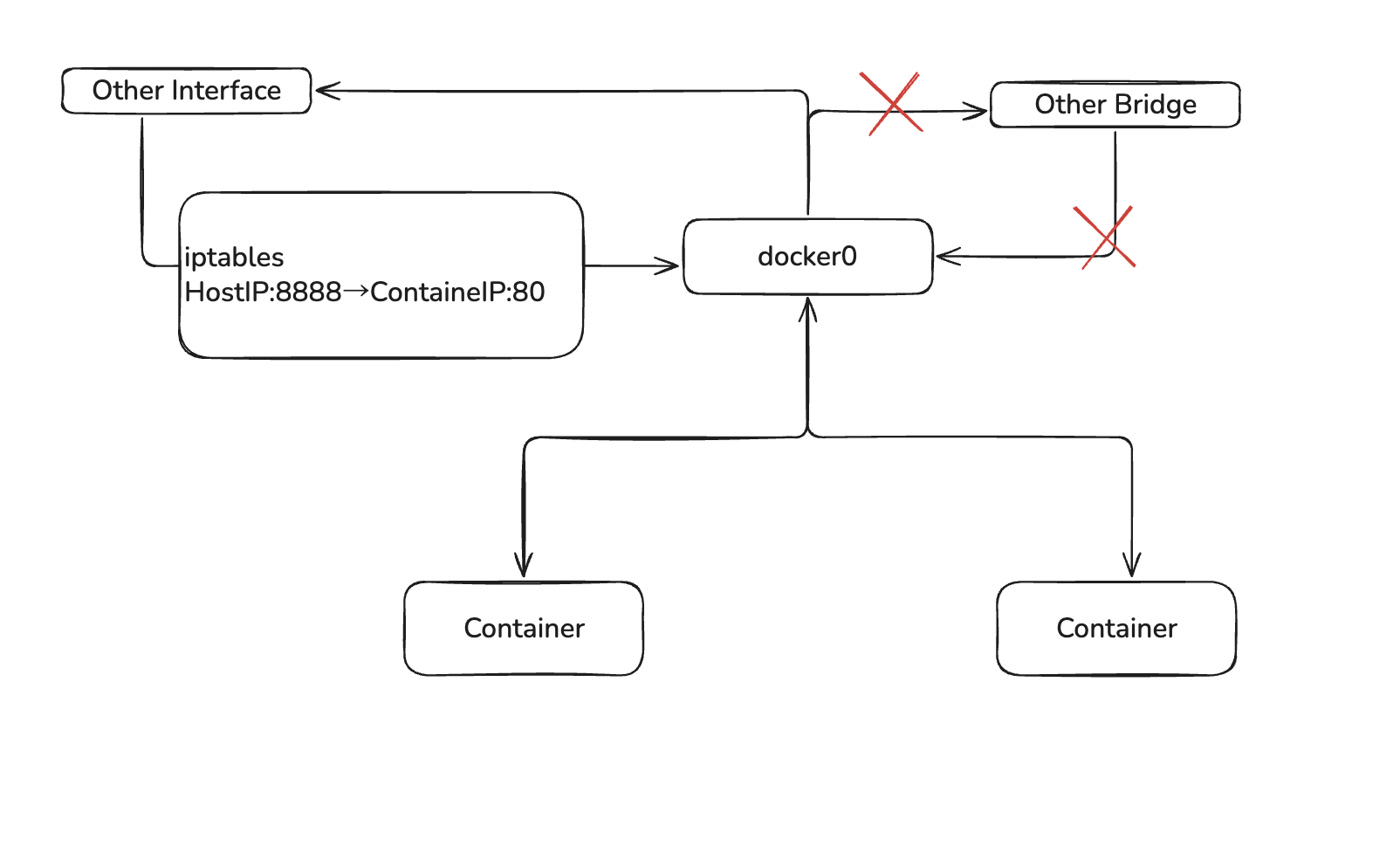
... "IPAddress": "172.17.0.2",まとめ
図で表すと下記のようになる。ホストIPの8888へのアクセスはコンテナのIPの80番ポートに流れる。
docker内の通信とdocker0からの外向きの通信のみ許可されている。